Abstract
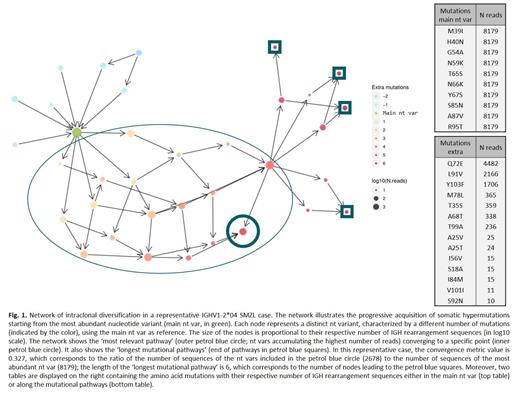
Almost one-third of all splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) cases express B cell receptor immunoglobulin (BcR IG) encoded by the IGHV1-2*04 gene. Such cases display a distinctive profile of genomic aberrations (e.g. higher incidence of NOTCH2 and KLF2 mutations) and a more aggressive clinical course compared to SMZL cases utilizing other IGHV genes. Such skewing of the BcR IG gene repertoire implicates antigen selection in SMZL ontogeny. Although the supportive evidence is compelling, it mostly derives from low-throughput approaches, which are inherently limited in their capacity to capture the complexity of the BcR IG gene repertoire. This hinders the comprehensive assessment of the subclonal architecture of SMZL that could offer insight into the dynamics of antigen-IG interactions. Here, we sought to overcome this limitation through a high-throughput immunogenetic investigation of SMZL, focusing on the detailed characterization of somatic hypermutation (SHM) and intraclonal diversification (ID) profiles. Our study included 22 cases utilizing the IGHV1-2*04 gene and 36 cases utilizing other IGHV genes. IGHV-IGHD-IGHJ (IGH) gene rearrangements were PCR-amplified and libraries were sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Data was analyzed with the IMGT/HighV-QUEST and TRIP software as well as a novel bioinformatics/biostatistics pipeline. Clonotypes were defined as unique combinations of a given IGHV gene+VH CDR3 amino acid (aa) sequence. Only IGH gene rearrangement sequences assigned to the dominant clonotypes of each case were assessed. In detail, all nucleotide variants (nt vars, i.e. all sequences clustered in the same dominant clonotype yet displaying distinct SHM profiles) were identified and further analyzed. Starting from the most abundant nt var, a network was built representing its connections with all other nt vars. For this analysis, we introduce the terms 'most relevant pathway' (MRP) corresponding to the pathway including connected nt vars with the highest total number of IGH sequences; and 'longest mutational pathways' (LMP) corresponding to the pathways with the highest number of nt vars (Fig. 1). Different graph metrics assessed the impact of ID in different SMZL subgroups: the first one focuses on the 'most relevant pathway' and quantifies SHM convergence [ratio of the total number of IGH sequences corresponding to the nt vars of this pathway to the number of IGH sequences in the most abundant nt var]; while the second refers to the length of the 'longest mutational pathways'.
Cases lacking additional connected nt vars [length of the LMP=1; 3 IGHV1-2*04 cases and 4 non-IGHV1-2*04 cases] were excluded. Consequently, the analysis included 19 IGHV1-2*04 cases and 32 non-IGHV1-2*04 cases. Significant differences were noted in the SHM and ID profiles between groups; the IGHV1-2*04 group had significantly (p<0.01) higher convergence values ranging from 0.009 to 1.243 (median: 0.102), as opposed to the non-IGHV1-2*04 group (range: 0.002-1.13, median: 0.014), overall suggesting that stronger selective pressures act in SMZL cases expressing the IGHV1-2*04 versus others. Moreover, IGHV1-2*04 cases displayed significantly (p<0.01) longer mutational pathways (length range: 2-6, median: 3) compared to the other group (range: 2-5, median: 2), alluding to more pronounced ID arising due to ongoing SHM.
Finally, all mutations leading to aa changes were analyzed in the context of ID networks. More recurrent aa mutations were identified amongst cases with higher levels of convergence. For instance, the VH FR2 M39I change, one of the most prominent recurrent SHMs in the IGHV1-2*04 group, was found in the most abundant nt var in 13/19 IGHV1-2*04 cases, while it was identified in nt vars with extra mutations in another 3 cases. Of interest, it was present at the end of the mutational pathways in these 16 cases, whilst in the other group it was present only in one case using the IGHV1-2*02 gene, and absent in the rest (p<0.01).
In conclusion, in the first large-scale high-throughput immunogenetic analysis of SMZL we provide strong evidence for more pronounced antigenic pressure in cases utilizing IGHV1-2*04 versus other IGHV genes. Our findings highlight a unique subclonal architecture for IGHV1-2*04 SMZL and corroborate the hypothesis that this group may represent a distinct molecular variant of SMZL.
Rossi: Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Verastem: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Cellestia: Honoraria, Research Funding. Chatzidimitriou: Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding. Stamatopoulos: Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal